Management Summary
Tezos contacted Sayfer Security in order to perform a security audit on Tezos MetaMask Snap in June 2023.
Before assessing the above services, we held a kickoff meeting with the Tezos technical team and received an overview of the system and the goals for this research.
Over the research period of 2 weeks, we discovered 4 findings in the system.
In conclusion, several fixes should be implemented following the report, but the system’s security posture is competent.
Vulnerabilities by Risk
High – Direct threat to key business processes.
Medium – Indirect threat to key business processes or partial threat to business processes.
Low – No direct threat exists. The vulnerability may be exploited using other vulnerabilities.
Informational – This finding does not indicate vulnerability, but states a comment that notifies about design flaws and improper implementation that might cause a problem in the long run.
Approach
Security Evaluation Methodology
Sayfer uses OWASP WSTG as our technical standard when reviewing web applications. After gaining a thorough understanding of the system we decided which OWASP tests are required to evaluate the system.
Security Assessment
After understanding and defining the scope, performing threat modeling, and evaluating the correct tests required in order to fully check the application for security flaws, we performed our security assessment.
Issue Table Description
Issue title
| ID | The OWASP ID of the issue. Additional tests that we conduct and are not included in the OWASP table will have Sayfer ID. Example ID: WSTG-INFO-002 WSTG – Web Security Test Guide. INFO – A shorthand for the topic to which the issue belongs. 002 – Issue number. |
| Risk | Represents the risk factor of the issue. For further description refer to the Vulnerabilities by Risk section. |
| Required Skill | Describes the skill level required to conduct successful exploitation. The lower the skill level the easier the exploitation process. |
| OWASP Reference |
A link to the relevant OWASP page for further knowledge. |
| Location | The URL in which this issue was detected. Issues with no location have no particular location and refer to the product as a whole. |
| Tools | The tools used to detect the issue. |
Description
Here we provide a brief description of the issue and how it formed, the steps we made to find or exploit it, along with proof of concept (if present), and how this issue can affect the product or its users. .
Mitigation
Suggested resolving options for this issue and links to advised sites for further remediation.
Security Evaluation
The following tests were conducted while auditing the system
Information Gathering
| Information Gathering | Test Name |
| WSTG-INFO-01 | Conduct Search Engine Discovery Reconnaissance for Information Leakage |
| WSTG-INFO-02 | Fingerprint Web Server |
| WSTG-INFO-03 | Review Webserver Metafiles for Information Leakage |
| WSTG-INFO-04 | Enumerate Applications on Webserver |
| WSTG-INFO-05 | Review Webpage Content for Information Leakage |
| WSTG-INFO-06 | Identify application entry points |
| WSTG-INFO-07 | Map execution paths through application |
| WSTG-INFO-08 | Fingerprint Web Application Framework |
| WSTG-INFO-09 | Fingerprint Web Application |
| WSTG-INFO-10 | Map Application Architecture |
Configuration and Deploy Management Testing
| Configuration and Deploy Management Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-CONF-01 | Test Network Infrastructure Configuration |
| WSTG-CONF-02 | Test Application Platform Configuration |
| WSTG-CONF-03 | Test File Extensions Handling for Sensitive Information |
| WSTG-CONF-04 | Review Old Backup and Unreferenced Files for Sensitive Information |
| WSTG-CONF-05 | Enumerate Infrastructure and Application Admin Interfaces |
| WSTG-CONF-06 | Test HTTP Methods |
| WSTG-CONF-07 | Test HTTP Strict Transport Security |
| WSTG-CONF-08 | Test RIA cross domain policy |
| WSTG-CONF-09 | Test File Permission |
| WSTG-CONF-10 | Test for Subdomain Takeover |
| WSTG-CONF-11 | Test Cloud Storage |
Identity Management Testing
| Identity Management Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-IDNT-01 | Test Role Definitions |
| WSTG-IDNT-02 | Test User Registration Process |
| WSTG-IDNT-03 | Test Account Provisioning Process |
| WSTG-IDNT-04 | Testing for Account Enumeration and Guessable User Account |
| WSTG-IDNT-05 | Testing for Weak or unenforced username policy |
Authentication Testing
| Authentication Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-ATHN-01 | Testing for Credentials Transported over an Encrypted Channel |
| WSTG-ATHN-02 | Testing for Default Credentials |
| WSTG-ATHN-03 | Testing for Weak Lock Out Mechanism |
| WSTG-ATHN-04 | Testing for Bypassing Authentication Schema |
| WSTG-ATHN-05 | Testing for Vulnerable Remember Password |
| WSTG-ATHN-06 | Testing for Browser Cache Weaknesses |
| WSTG-ATHN-07 | Testing for Weak Password Policy |
| WSTG-ATHN-08 | Testing for Weak Security Question Answer |
| WSTG-ATHN-09 | Testing for Weak Password Change or Reset Functionalities |
| WSTG-ATHN-10 | Testing for Weaker Authentication in Alternative Channel |
Authorization Testing
| Authorization Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-ATHZ-01 | Testing Directory Traversal File Include |
| WSTG-ATHZ-02 | Testing for Bypassing Authorization Schema |
| WSTG-ATHZ-03 | Testing for Privilege Escalation |
| WSTG-ATHZ-04 | Testing for Insecure Direct Object References |
Session Management Testing
| Session Management Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-SESS-01 | Testing for Session Management Schema |
| WSTG-SESS-02 | Testing for Cookies Attributes |
| WSTG-SESS-03 | Testing for Session Fixation |
| WSTG-SESS-04 | Testing for Exposed Session Variables |
| WSTG-SESS-05 | Testing for Cross Site Request Forgery |
| WSTG-SESS-06 | Testing for Logout Functionality |
| WSTG-SESS-07 | Testing Session Timeout |
| WSTG-SESS-08 | Testing for Session Puzzling |
| WSTG-SESS-09 | Testing for Session Hijacking |
Data Validation Testing
| Data Validation Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-INPV-01 | Testing for Reflected Cross Site Scripting |
| WSTG-INPV-02 | Testing for Stored Cross Site Scripting |
| WSTG-INPV-03 | Testing for HTTP Verb Tampering |
| WSTG-INPV-04 | Testing for HTTP Parameter Pollution |
| WSTG-INPV-05 | Testing for SQL Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-06 | Testing for LDAP Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-07 | Testing for XML Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-08 | Testing for SSI Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-09 | Testing for XPath Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-10 | Testing for IMAP SMTP Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-11 | Testing for Code Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-12 | Testing for Command Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-13 | Testing for Format String Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-14 | Testing for Incubated Vulnerability |
| WSTG-INPV-15 | Testing for HTTP Splitting Smuggling |
| WSTG-INPV-16 | Testing for HTTP Incoming Requests |
| WSTG-INPV-17 | Testing for Host Header Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-18 | Testing for Server-side Template Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-19 | Testing for Server-Side Request Forgery |
Error Handling
| Error Handling | Test Name |
| WSTG-ERRH-01 | Testing for Improper Error Handling |
| WSTG-ERRH-02 | Testing for Stack Traces |
Cryptography
| Cryptography | Test Name |
| WSTG-CRYP-01 | Testing for Weak Transport Layer Security |
| WSTG-CRYP-02 | Testing for Padding Oracle |
| WSTG-CRYP-03 | Testing for Sensitive Information Sent via Unencrypted Channels |
| WSTG-CRYP-04 | Testing for Weak Encryption |
Business logic Testing
| Business logic Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-BUSL-01 | Test Business Logic Data Validation |
| WSTG-BUSL-02 | Test Ability to Forge Requests |
| WSTG-BUSL-03 | Test Integrity Checks |
| WSTG-BUSL-04 | Test for Process Timing |
| WSTG-BUSL-05 | Test Number of Times a Function Can be Used Limits |
| WSTG-BUSL-06 | Testing for the Circumvention of Work Flows |
| WSTG-BUSL-07 | Test Defenses Against Application Mis-use |
| WSTG-BUSL-08 | Test Upload of Unexpected File Types |
| WSTG-BUSL-09 | Test Upload of Malicious Files |
Client Side Testing
| Client Side Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-CLNT-01 | Testing for DOM-Based Cross Site Scripting |
| WSTG-CLNT-02 | Testing for JavaScript Execution |
| WSTG-CLNT-03 | Testing for HTML Injection |
| WSTG-CLNT-04 | Testing for Client Side URL Redirect |
| WSTG-CLNT-05 | Testing for CSS Injection |
| WSTG-CLNT-06 | Testing for Client Side Resource Manipulation |
| WSTG-CLNT-07 | Test Cross Origin Resource Sharing |
| WSTG-CLNT-08 | Testing for Cross Site Flashing |
| WSTG-CLNT-09 | Testing for Clickjacking |
| WSTG-CLNT-10 | Testing WebSockets |
| WSTG-CLNT-11 | Test Web Messaging |
| WSTG-CLNT-12 | Testing Browser Storage |
| WSTG-CLNT-13 | Testing for Cross Site Script Inclusion |
API Testing
| API Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-APIT-01 | Testing GraphQL |
Order audit from Sayfer
Security Assessment Findings
Dependencies with Known Vulnerabilities
| ID | SAY-01 |
| Status | Fixed |
| Risk | Low |
| Location | – |
| Business Impact | Using vulnerable versions of node modules could expose the service to various attacks, some of them less critical, but others severe. |
Description
The NPM audit returns multiple results for known vulnerabilities in the installed packages:
npm audit
# npm audit report
engine.io 5.1.0 - 6.4.1
Severity: moderate
engine.io Uncaught Exception vulnerability -
https://github.com/advisories/GHSA-q9mw-68c2-j6m5
fix available via `npm audit fix`
node_modules/engine.io
socket.io 4.1.0 - 4.6.0-alpha1
Depends on vulnerable versions of engine.io
node_modules/socket.io
gatsby 1.9.130 - 4.25.7 || 5.4.0-next.0 - 5.9.1
Depends on vulnerable versions of gatsby-cli
Depends on vulnerable versions of latest-version
Depends on vulnerable versions of socket.io
node_modules/gatsby
got <11.8.5
Severity: moderate
Got allows a redirect to a UNIX socket -
https://github.com/advisories/GHSA-pfrx-2q88-qq97
fix available via `npm audit fix`
node_modules/package-json/node_modules/got
package-json <=6.5.0
Depends on vulnerable versions of got
node_modules/package-json
latest-version 0.2.0 - 5.1.0
Depends on vulnerable versions of package-json
node_modules/latest-version
update-notifier 0.2.0 - 5.1.0
Depends on vulnerable versions of latest-version
node_modules/update-notifier
gatsby-cli 1.1.27 - 4.25.0
Depends on vulnerable versions of update-notifier
node_modules/gatsby-cli
13
request *
Severity: moderate
Server-Side Request Forgery in Request -
https://github.com/advisories/GHSA-p8p7-x288-28g6
fix available via `npm audit fix`
node_modules/request
node-gyp <=7.1.2
Depends on vulnerable versions of request
node_modules/@npmcli/run-script/node_modules/node-gyp
@npmcli/run-script 1.1.1 - 1.8.6
Depends on vulnerable versions of node-gyp
node_modules/@npmcli/run-script
@lavamoat/allow-scripts <=2.3.0
Depends on vulnerable versions of @npmcli/run-script
node_modules/@lavamoat/allow-scripts
socket.io-parser 4.0.4 - 4.2.2
Severity: high
Insufficient validation when decoding a Socket.IO packet -
https://github.com/advisories/GHSA-cqmj-92xf-r6r9
fix available via `npm audit fix`
node_modules/socket.io-parser
webpack 5.0.0 - 5.75.0
Severity: high
Cross-realm object access in Webpack 5 -
https://github.com/advisories/GHSA-hc6q-2mpp-qw7j
fix available via `npm audit fix`
node_modules/webpack
yaml 2.0.0-5 - 2.2.1
Severity: high
Uncaught Exception in yaml - https://github.com/advisories/GHSA-f9xv-q969-pqx4
fix available via `npm audit fix`
node_modules/yaml-loader/node_modules/yaml We validated each one of them to make sure it is not affecting the production build, and found that even the high-severity ones do not have a direct effect on Tezos Snap. While this means there is no security risk right now, new features or new vulnerabilities might happen in the future.
Mitigation
The first step would be to update the packages to the versions where possible On a bigger picture level, there is a need for an automated system to alert about new vulnerabilities and a process should be in place to mitigate them when critical ones arise.
Magic Numbers
| ID | SAY-02 |
| Status | Fixed |
| Risk | Informational |
| Location | – |
| Business Impact | Magic numbers impact code readability. Without inside knowledge, they appear to be rather arbitrary. |
Description
During our assessment, we noticed the usage of seemingly arbitrary constants without explanatory comments:
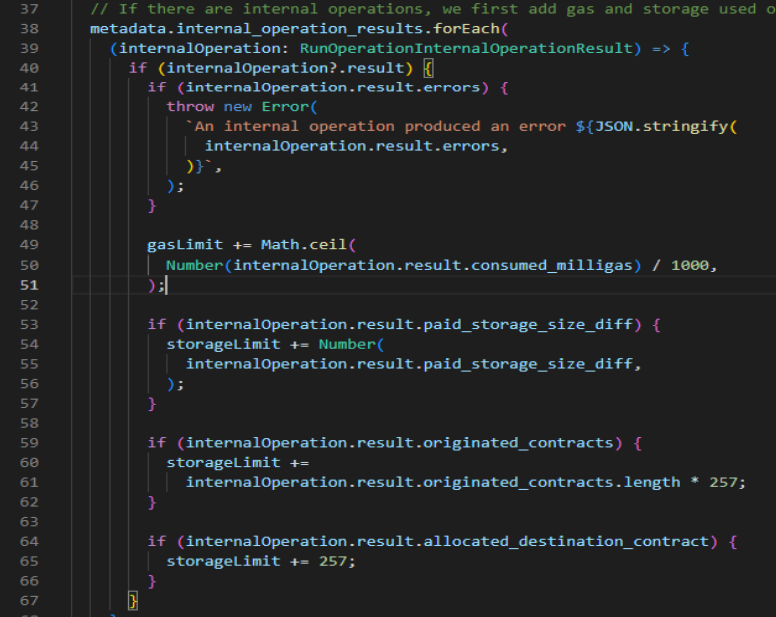
In the case above, it’s hard to guess what is the reason for dividing by 1000 or multiplying by 257 without knowing how the protocol and the blockchain itself work
Mitigation
It’s considered good practice to give such hard-coded constants descriptive names, and if necessary, to add explanatory comments.
Alarming Metamask Prompt
| ID | SAY-03 |
| Status | Fixed |
| Risk | Informational |
| Location | – |
| Business Impact | This kind of prompt may dissuade users from installing Snap |
Description
When installing Snap the following hard-to-understand metamask prompt appears:
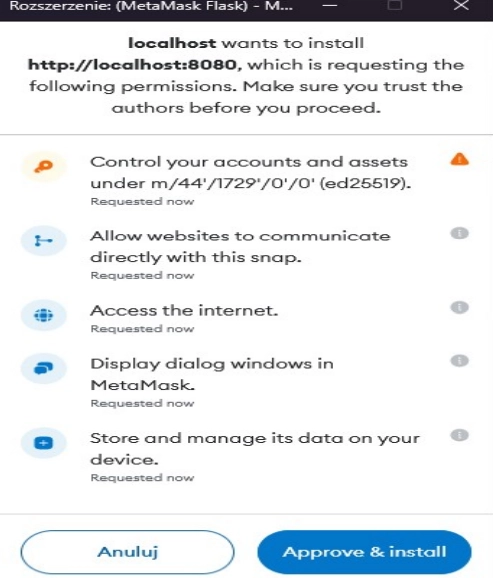
Mitigation
It may not be possible for Tezos to change this rather scary prompt. However, since it may be of interest, we decided to include this issue as informational.
Alarming Metamask Prompt
| ID | SAY-04 |
| Status | Fixed |
| Risk | Informational |
| Location | – |
| Business Impact | None |
Description
During our assessment, we noticed this comment, implying a certain uncertainty, which might point to an underlying bigger issue
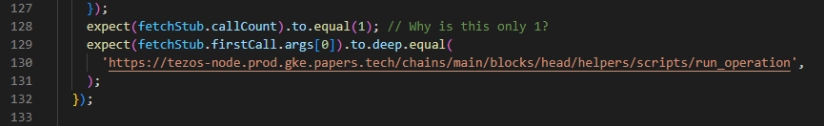
We investigated and couldn’t verify what’s the issue here the comment referring about.
Mitigation
These comments should be changed or removed on the release version, or if there is a deeper issue here, the developers should update the logic of why this
Appendix A: Security Evaluation Fixes
After a review by the Sayfer team, we can confirm that all the vulnerabilities have been fixed by the Tezos team
Initial commit hash: 0e0d653b85cbd11365771ad9c2ee5726b10a7d26
Fixes commit hash: 0d0c9381a1107c54647d927d4fe99694f332e24d