Management Summary
XRPL Snap contacted Sayfer Security in order to perform penetration testing on XRPL’s MetaMask Snap in January 2024.
Before assessing the above services, we held a kickoff meeting with the XRPL Snap technical team and received an overview of the system and the goals for this research.
Over the research period of 2 weeks, we discovered 7 vulnerabilities in the system.
In conclusion, several fixes should be implemented following the report, but the system’s security posture is competent.
After a review by the Sayfer team, we certify that all the security issues mentioned in this report have been addressed by the XRPL Snap team.
Risk Methodology
At Sayfer, we are committed to delivering the highest quality penetration testing to our clients. That’s why we have implemented a comprehensive risk assessment model to evaluate the severity of our findings and provide our clients with the best possible recommendations for mitigation.
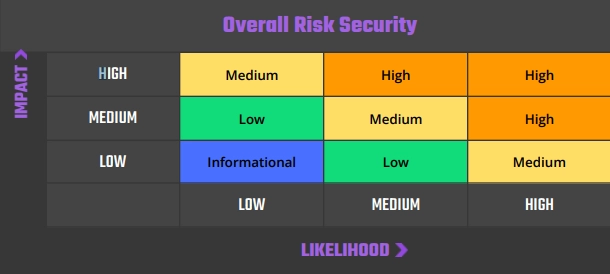
Our risk assessment model is based on two key factors: IMPACT and LIKELIHOOD. Impact refers to the potential harm that could result from an issue, such as financial loss, reputational damage, or a non-operational system. Likelihood refers to the probability that an issue will occur, taking into account factors such as the complexity of the attack and the number of potential attackers.
By combining these two factors, we can create a comprehensive understanding of the risk posed by a particular issue and provide our clients with a clear and actionable assessment of the severity of the issue. This approach allows us to prioritize our recommendations and ensure that our clients receive the best possible advice on how to protect their business.
Risk is defined as follows:
Vulnerabilities by Risk
High – Direct threat to key business processes.
Medium – Indirect threat to key business processes or partial threat to business processes.
Low – No direct threat exists. The vulnerability may be exploited using other vulnerabilities.
Informational – This finding does not indicate vulnerability, but states a comment that notifies about design flaws and improper implementation that might cause a problem in the long run.
Approach
Security Evaluation Methodology
Sayfer uses OWASP WSTG as our technical standard when reviewing web applications. After gaining a thorough understanding of the system we decided which OWASP tests are required to evaluate the system.
Security Assessment
After understanding and defining the scope, performing threat modeling, and evaluating the correct tests required in order to fully check the application for security flaws, we performed our security assessment.
Issue Table Description
Issue title
| ID | SAY-??: An ID for easy communication on each vulnerability |
| Status | Open/Fixed/Acknowledged |
| Risk | Represents the risk factor of the issue. For further description refer to the Vulnerabilities by Risk section. |
| Business Impact | The main risk of the vulnerability at a business level. |
| Location | The URL or the file in which this issue was detected. Issues with no location have no particular location and refer to the product as a whole. |
Description
Here we provide a brief description of the issue and how it formed, the steps we made to find or exploit it, along with proof of concept (if present), and how this issue can affect the product or its users.
Mitigation
Suggested resolving options for this issue and links to advised sites for further remediation.
Security Evaluation
The following tests were conducted while auditing the system
Information Gathering
| Information Gathering | Test Name |
| WSTG-INFO-01 | Conduct Search Engine Discovery Reconnaissance for Information Leakage |
| WSTG-INFO-02 | Fingerprint Web Server |
| WSTG-INFO-03 | Review Webserver Metafiles for Information Leakage |
| WSTG-INFO-04 | Enumerate Applications on Webserver |
| WSTG-INFO-05 | Review Webpage Content for Information Leakage |
| WSTG-INFO-06 | Identify application entry points |
| WSTG-INFO-07 | Map execution paths through application |
| WSTG-INFO-08 | Fingerprint Web Application Framework |
| WSTG-INFO-09 | Fingerprint Web Application |
| WSTG-INFO-10 | Map Application Architecture |
Configuration and Deploy Management Testing
| Configuration and Deploy Management Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-CONF-01 | Test Network Infrastructure Configuration |
| WSTG-CONF-02 | Test Application Platform Configuration |
| WSTG-CONF-03 | Test File Extensions Handling for Sensitive Information |
| WSTG-CONF-04 | Review Old Backup and Unreferenced Files for Sensitive Information |
| WSTG-CONF-05 | Enumerate Infrastructure and Application Admin Interfaces |
| WSTG-CONF-06 | Test HTTP Methods |
| WSTG-CONF-07 | Test HTTP Strict Transport Security |
| WSTG-CONF-08 | Test RIA cross domain policy |
| WSTG-CONF-09 | Test File Permission |
| WSTG-CONF-10 | Test for Subdomain Takeover |
| WSTG-CONF-11 | Test Cloud Storage |
Identity Management Testing
| Identity Management Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-IDNT-01 | Test Role Definitions |
| WSTG-IDNT-02 | Test User Registration Process |
| WSTG-IDNT-03 | Test Account Provisioning Process |
| WSTG-IDNT-04 | Testing for Account Enumeration and Guessable User Account |
| WSTG-IDNT-05 | Testing for Weak or unenforced username policy |
Authentication Testing
| Authentication Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-ATHN-01 | Testing for Credentials Transported over an Encrypted Channel |
| WSTG-ATHN-02 | Testing for Default Credentials |
| WSTG-ATHN-03 | Testing for Weak Lock Out Mechanism |
| WSTG-ATHN-04 | Testing for Bypassing Authentication Schema |
| WSTG-ATHN-05 | Testing for Vulnerable Remember Password |
| WSTG-ATHN-06 | Testing for Browser Cache Weaknesses |
| WSTG-ATHN-07 | Testing for Weak Password Policy |
| WSTG-ATHN-08 | Testing for Weak Security Question Answer |
| WSTG-ATHN-09 | Testing for Weak Password Change or Reset Functionalities |
| WSTG-ATHN-10 | Testing for Weaker Authentication in Alternative Channel |
Authorization Testing
| Authorization Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-ATHZ-01 | Testing Directory Traversal File Include |
| WSTG-ATHZ-02 | Testing for Bypassing Authorization Schema |
| WSTG-ATHZ-03 | Testing for Privilege Escalation |
| WSTG-ATHZ-04 | Testing for Insecure Direct Object References |
Session Management Testing
| Session Management Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-SESS-01 | Testing for Session Management Schema |
| WSTG-SESS-02 | Testing for Cookies Attributes |
| WSTG-SESS-03 | Testing for Session Fixation |
| WSTG-SESS-04 | Testing for Exposed Session Variables |
| WSTG-SESS-05 | Testing for Cross Site Request Forgery |
| WSTG-SESS-06 | Testing for Logout Functionality |
| WSTG-SESS-07 | Testing Session Timeout |
| WSTG-SESS-08 | Testing for Session Puzzling |
| WSTG-SESS-09 | Testing for Session Hijacking |
Data Validation Testing
| Data Validation Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-INPV-01 | Testing for Reflected Cross Site Scripting |
| WSTG-INPV-02 | Testing for Stored Cross Site Scripting |
| WSTG-INPV-03 | Testing for HTTP Verb Tampering |
| WSTG-INPV-04 | Testing for HTTP Parameter Pollution |
| WSTG-INPV-05 | Testing for SQL Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-06 | Testing for LDAP Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-07 | Testing for XML Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-08 | Testing for SSI Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-09 | Testing for XPath Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-10 | Testing for IMAP SMTP Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-11 | Testing for Code Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-12 | Testing for Command Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-13 | Testing for Format String Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-14 | Testing for Incubated Vulnerability |
| WSTG-INPV-15 | Testing for HTTP Splitting Smuggling |
| WSTG-INPV-16 | Testing for HTTP Incoming Requests |
| WSTG-INPV-17 | Testing for Host Header Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-18 | Testing for Server-side Template Injection |
| WSTG-INPV-19 | Testing for Server-Side Request Forgery |
Error Handling
| Error Handling | Test Name |
| WSTG-ERRH-01 | Testing for Improper Error Handling |
| WSTG-ERRH-02 | Testing for Stack Traces |
Cryptography
| Cryptography | Test Name |
| WSTG-CRYP-01 | Testing for Weak Transport Layer Security |
| WSTG-CRYP-02 | Testing for Padding Oracle |
| WSTG-CRYP-03 | Testing for Sensitive Information Sent via Unencrypted Channels |
| WSTG-CRYP-04 | Testing for Weak Encryption |
Business logic Testing
| Business logic Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-BUSL-01 | Test Business Logic Data Validation |
| WSTG-BUSL-02 | Test Ability to Forge Requests |
| WSTG-BUSL-03 | Test Integrity Checks |
| WSTG-BUSL-04 | Test for Process Timing |
| WSTG-BUSL-05 | Test Number of Times a Function Can be Used Limits |
| WSTG-BUSL-06 | Testing for the Circumvention of Work Flows |
| WSTG-BUSL-07 | Test Defenses Against Application Mis-use |
| WSTG-BUSL-08 | Test Upload of Unexpected File Types |
| WSTG-BUSL-09 | Test Upload of Malicious Files |
Client Side Testing
| Client Side Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-CLNT-01 | Testing for DOM-Based Cross Site Scripting |
| WSTG-CLNT-02 | Testing for JavaScript Execution |
| WSTG-CLNT-03 | Testing for HTML Injection |
| WSTG-CLNT-04 | Testing for Client Side URL Redirect |
| WSTG-CLNT-05 | Testing for CSS Injection |
| WSTG-CLNT-06 | Testing for Client Side Resource Manipulation |
| WSTG-CLNT-07 | Test Cross Origin Resource Sharing |
| WSTG-CLNT-08 | Testing for Cross Site Flashing |
| WSTG-CLNT-09 | Testing for Clickjacking |
| WSTG-CLNT-10 | Testing WebSockets |
| WSTG-CLNT-11 | Test Web Messaging |
| WSTG-CLNT-12 | Testing Browser Storage |
| WSTG-CLNT-13 | Testing for Cross Site Script Inclusion |
API Testing
| API Testing | Test Name |
| WSTG-APIT-01 | Testing GraphQL |
Order audit from Sayfer
Security Assessment Findings
[M] SignHelper(string, any) Fails to Return an Error
| ID | SAY-01 |
| Status | Fixed |
| Risk | Medium |
| Business Impact | If the API returns an error related to the risk classification, the transaction will not be terminated, which may lead to incomplete information to the user about the potential risk. |
| Location | – src/handler/sign-transaction.ts:47; SignHelper(string, any) |
Description
SignHelper(string, any) calls on TransactionRisk(string), in order to verify via the offchain API whether the transaction’s destination has suspicious history. Based on this, a certain classification is returned, which is then returned to the user on the screen. If this operation returns an unspecified error, the SignHelper function will catch it with a try-catch statement. However, the catch block does not perform any action, so this error will be ignored and the user will receive unplanned output on the screen.
- SignHelper(string, any)
try {
xrplorerTransactionRisk = await SignTransaction.TransactionRisk(
payment.Destination,
);
} catch (err) {}Mitigation
In the event of an error on the API side, a message should be displayed to the user, or conversely the transaction should be aborted altogether.
[M] Dysfunctional Hardcoded Domain
| ID | SAY-02 |
| Status | Fixed |
| Risk | Medium |
| Business Impact | An incorrectly functioning API without the ability to edit it from the configuration level may render the snap unusable. |
| Location | – src/handler/sign-transaction.ts:18; TransactionRisk(string) |
Description
As part of the risk classification process, a certain hardcoded URL is queried. During our testing attempts were made to verify several sample addresses in order to analyze the behavior of the API, but each time, it returned a code 500 error. Therefore, it was not possible to verify whether the risk classification process is working correctly. Additionally, there is no way to change this domain to another one (without modifying the code) because it is hardcoded.
- TransactionRisk(string)
private static TransactionRisk(address: string) {
return fetch(
https://europe-west3-xrpl-snap-366820.cloudfunctions.net/proxy-to-xrpl-forensics?address=${address}`,
{
method: 'GET',
mode: 'cors',
redirect: 'follow',
},
).then((response) => response.json());
}Mitigation
We suggest you verify why the server is not working properly. Additionally, we recommend adding an option to configure the domain on which the API operates, as well as checking its behavior for various token addresses.
[L] No-Null Assertions Can Be Avoided
| ID | SAY-03 |
| Status | Fixed |
| Risk | Low |
| Business Impact | Using no-null assertions (!) is considered a poor practice because having to rely on them to provide information to the type checker implies that the code is not entirely type-safe. Usually, one can structure their code so that the TypeScript compiler can infer when values may be null. |
| Location | – src/transactions/offer-cancel.ts:20 – src/transactions/payment.ts:34 – src/transactions/trustset.ts:19 – src/xrpl/wallet.ts:14 – src/xrpl/wallet.ts:16 – src/xrpl/wallet.ts:17 |
Description
Description In several cases, the snap uses non-null assertions, which are considered a bad security practice. A more stringent approach is to use the optional chaining operator (?), which automatically checks whether the element before it is `null` or `undefined`. If this is the case, the entire expression returns undefined, rather than throwing an error when we try to reference a property or call a method on null or undefined values.
Mitigation
Mitigation We recommend changing the implementation and implementing the chaining operator (?) instead of non-null assertions (!).
[L] Test scenarios and unit tests are missing
| ID | SAY-04 |
| Status | Fixed |
| Risk | Low |
| Business Impact | Test scenarios and unit tests are an excellent way for developers to preempt bugs and security vulnerabilities. |
| Location | – src/handler/account-transactions.ts; handleLimitParameter(number) – src/handler/account-transactions.ts:24; handler(string, any) – src/xrpl/client.ts:11 |
Description
The snap has specification tests for each of the files in src/handler and src/transactions, and several in src/xrpl. However, they do not fully cover all functionalities and features found in the codebase.
Moreover, there is a lack of complete and accurate end-to-end tests and verification of various test scenarios, such as signing and sending transactions with different inputs.
Mitigation
We suggest covering the entire code with tests to ensure that it has been implemented in accordance with the assumed business and functional logic.
[I] Leftover TODOs
| ID | SAY-05 |
| Status | Fixed |
| Risk | Informational |
| Business Impact | While this finding has no security ramifications (and was therefore classified as informational), leftover TODOs scattered throughout the code imply that the development cycle of the snap is not yet complete. |
| Location | – src/xrpl/transaction.ts:38, 66 – src/handler/sign-submit-transaction.ts:5 |
Description
Description During our research, we found three instances of TODO comments scattered throughout the snap code.
Mitigation
Mitigation We suggest that you resolve all comments marked as TODO, or use an internal, non-public list of places where the code is not finished in production.
[I] Non-functioning Demo
| ID | SAY-06 |
| Status | Fixed |
| Risk | Informational |
| Business Impact | Potential users may be confused if the snap does not work by default after executing `yarn install && yarn start`. |
| Location | — |
Description
Description When trying to install Snap in the default configuration, an error is returned indicating that version 0.1.0 is not compatible with the expected version 0.3.2. While this can be easily rectified, new and especially non-technical users may find this confusing.
Mitigation
Mitigation We suggest customizing your Snap configuration so that it runs by default after you build and install it.
[I] Unimplemented Demo Methods
| ID | SAY-07 |
| Status | Fixed |
| Risk | Informational |
| Business Impact | Potential users may find it confusing that some functionalities in the demo are not actually working. Another risk is that these functionalities were supposed to be implemented, but were forgotten. |
| Location | — |
Description
Two methods in the demo are not actually supported by the code. These are “Transaction Info” and “Get NFTs”. There are no handlers that could handle such functionalities.
export const getAccountNfts = async (address?: string) => {
console.log('get NFTs', address);return await window.ethereum.request({
method: 'wallet_invokeSnap',
params: {
snapId: SNAP_ENDPOINT,
request: {
method: 'xrpl_accountNfts',
params: { address },
}
},
});
};export const getTransactionInfo = async (transactionHash?: string) => {
console.log('get transaction info', transactionHash, SNAP_ENDPOINT);
return await window.ethereum.request({
method: 'wallet_invokeSnap',
params: {
snapId: SNAP_ENDPOINT,
request: {
method: 'xrpl_transactionInfo',
params: { transactionHash }
}
}
});
};Mitigation
Mitigation We recommend either removing these functionalities from the demo or conversely, actually implementing them.